Electronics Area – Electrical and Electronics Tutorials and Circuits
Welcome to Electronics Area
Electrical and Electronics Tutorials and Circuits
Recent posts
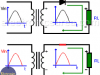
Half Wave Rectifier – Half-wave Rectifier. Circuit diagram
The half-wave rectifier rectification process. Polarization of semiconductor diode in the forward and in the reverse direction. Input and output waveforms
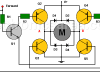
H-Bridge DC Motor Control Circuit
This circuit allows us to apply voltage to a DC motor in either direction (forward or reverse) using a control circuit.
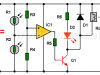
Shadow detector alarm circuit with two LDRs
Shadow detector alarm circuit with two LDRs
This circuit detects if there is a difference of lighting between two LDRs, and sends an audible and visual warning. Circuits that use two LDRs are more reliable than those that use only one.
Automatic Water Level Controler Circuit
This circuit ensures that an elevated tank always has enough amount of water. Perfect for 2 or more stories buildings or houses
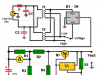
4 Amp Variable Power Supply Using the LM317
This variable power supply using an LM317 and a boost transistor can be useful when we need more current than the 1.5 amps that an LM317 can provide.
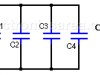
Capacitors in Series – Capacitors in Parallel
Capacitors in series – Capacitors in parallel. How to obtain the equivalent capacitance of series capacitors and parallel capacitors? Formulas and examples
Temperature Alarm using thermostats
Temperature Alarm using thermostats
This simple alarm with thermostats circuit can be used on places where we must detect overheating. It uses 3 thermostats, and a one 2 contact, relay
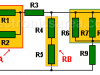
Series/Parallel Resistor Reduction
Series/Parallel Resistor Reduction. Resistors reduction can be done, making some simplifications using resistors in series and resistors in parallel formulas.
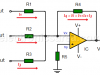
Inverting Summing Amplifier using Op Amp
The inverting summing amplifier using op amp outputs a voltage equal to the sum of the voltages it has in its inputs. The explanation is based on an adder of three inputs, but applies to an adder of any number of inputs
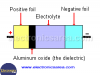
Electrolytic Capacitor
The Electrolytic Capacitor has been developed to achieve large capacities in small physical dimensions. To achieve this large capacity, a special dielectric is used.
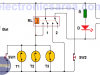
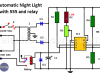
Automatic Night Light with 555 and relay
This automatic night light using 555 IC turns on lights when there is no daylight. The circuit is perfect for lighting single places such as the garden, the front door of the house, the entrance to the garage, etc.
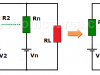
Millman’s Theorem – Millman’s equivalent circuit
Millman’s theorem is used to directly obtain the voltage between the ends of a parallel branch circuit. Equivalent Millman circuit Formulas, example.