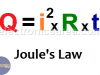Electronics Area – Electrical and Electronics Tutorials and Circuits
Welcome to Electronics Area
Electrical and Electronics Tutorials and Circuits
Recent posts
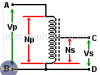
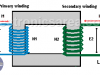
Transformer Structure
Electric Power Transformer Structure. All electric transformers, have three fundamentals parts: high voltage winding, low voltage winding and Core.
Autotransformer
An autotransformer is a transformer where a part of the winding belongs to both the primary and secondary windings of the transformer. The operating principle is the same as the conventional transformer.
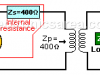
Impedance matching Transformer
An impedance matching transformer is used to couple an antenna to a transmission and / or reception equipment. It was widely used in the coupling of the antenna to the analog television, by radio amateurs
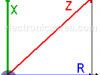
Impedance (Z) = (Resistance + Reactance)
Impedance (Z) shows the opposition to the flow of direct or alternating current. Impedance is the vector addition of resistance (R) and reactance (X).
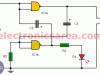
Clock signal generator using 7400 IC (PCB)
Clock signal generator using 7400 IC. This clock generator is an astable circuit which uses the TTL 7400 (four 2 inputs NAND gates) integrated circuit. Suggested Printed Circuit Board (PCB)
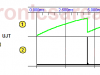
UJT Relaxation oscillator circuit
The UJT relaxation oscillator circuit is a non-linear oscillator used to generate a non-sinusoidal repetitive output signals that can trigger power control devices such as SCRs and TRIACs.
Joule’s Law. Joule’s Law formula
What is Joule’s Law?
It is known as Joule effect to the phenomenon by which if in a wire circulates an electrical current, part of the energy is transformed into heat. This law (Joule’s Law) is named after the British physicist James Prescott Joule.
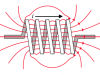
Inductor – Inductance
Inductor – Coil. Inductance units. The inductor is made of a conductive wire wrapped into a spring like form. Magnetic field lines – Counter electromotive force (CEMF)
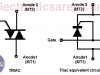
TRIAC – Power Control on AC
TRIAC. Power control on alternating current (AC)
Triac is a semiconductor device that belongs to the family of thyristor control devices. It is essentially two SCR connected in parallel and backwards, sharing the same gate.
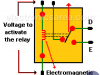
Relay – Electromagnetic Switch
What is a relay?
Relay was invented in 1835 by the US scientist Joseph Henry (1797–1878). Relay or elecromagnetic relay is a magnetically operated switch that is activated or deactivated when the electromagnet is energized.
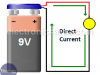
What is Direct Current? – What is DC?
Direct Current (DC), is the result of the flow of electrons (negative charge) in a conductor (most of the time, wires of copper) that goes only in one direction.
Transformer Turn Ratio (K)
The transformer turn ratio (K) is the quotient value obtained by dividing the number of turns of the primary winding (N1) and the number of turns of the secondary winding (N2). Then K = N1/N2.