Semiconductors
Home /
What is a semiconductor?
Semiconductors, sometimes called integrated circuits (ICs), are usually made of pure elements, typically silicon or germanium. The semiconductors conduct more electricity than an insulator, such as glass, but less than a pure conductor, such as copper.
In a process called doping, small amounts of impurities are added to these pure elements, causing large changes in the material’s conductivity. In other words, controlling the amount of current that pass through the material.
What are semiconductors used for?
Semiconductors are employed to make a lot of electronic devices, including diodes, transistors, and integrated circuits. Semiconductors are used in a lot of electronic products, as such as computers, tablets, smartphones, appliances, etc.
Diodes | |
|---|---|
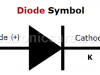 | The Semiconductor DiodeThe semiconductor diode is the simplest semiconductor device and can be found in almost any electronic circuit. Diodes are manufactured with germanium and silicon. |
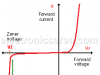
Zener diode – Basic Operation – ApplicationsThe Zener diode is a special type of semiconductor device that allows the flow of current on the opposite direction of the arrow of the diode. | |
Photodiode – How does it work?Photodiodes produce a leakage current that is directly proportional to light intensity. This leakage current flows in the opposite direction to the current in a conventional diode. | |
 | Schottky Diode (Schottky Barrier Diode)These diodes are characterized by their switching speed and low voltage drop when they are forward biased. (typically 0.25 to 0.4 volts) |
LED – Light-emitting diodeLED – Light-emitting diode Light-emitting diode (LED) is a special type of diode, that emits light when it is forward biased. | |
 | 7-segment DisplayThis component used to show numbers in many electronic devices. It is very common to find LCDs in much electronic equipment, but there are many that still use the 7-segment display for its simplicity. |
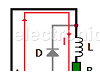 | Why is there a diode connected in parallel to a relay coil?The purpose of a diode connected in parallel to a relay coil (flywheel diode or freewheeling diode) is to avoid damaging some nearby components sensitive to high voltage. |
Transistors | |
|---|---|
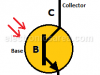 | What is a Phototransistor? – Equivalent CircuitA phototransistor is a transistor that can work in two different ways: as a common transistor and as a phototransistor, using the light that illuminates this element as the base current. |
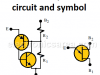 | UJT – Unijunction Transistor – Equivalent model & circuitThe UJT or Unijunction transistor is constituted by two polluted regions, with three external terminals: two bases and one emitter. |
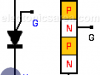 | PUT – Programmable Unijunction TransistorPUT – Programmable Unijunction Transistor. Main characteristics. PUT and UJT. Oscillator circuit design and waveforms. Frequency formula |
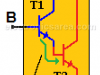 | Darlington transistorThe Darlington transistor is a special type of transistor with a high current gain. It consists of two internally bipolar transistors being connected in cascade |
Ebers Moll Model of a Bipolar TransistorEbers and Moll created a model between the current and voltages in the transistor terminals. This model is knowned as the Ebers Moll model | |
Optocoupler (LED and phototransistor)The Optocoupler is a device that consists of a LED and a phototransistor. When the LED emits light, it illuminates the phototransistor causing a current to flow through it. | |
 | FET – Field Effect Transistor (JFET)Field effect transistor or FET is a particularly interesting transistor and it can be of two types: the Junction Field Effect Transistor or JFET and the Metal-Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET). |
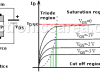 | FET Characteristics (N-channel JFET)The N-channel JFET consists of a silicon bar of N-type semiconductor with two P type regions on both sides. JFET is a tri-terminal device whose terminals are called drain, source and gate. |
JFET Saturation and Breakdown regionsJFET Saturation and Breakdown regions The JFET Saturation region In this region the JFET has some linear features that are used in amplification. | |
JFET Cutoff and Linear regionsJFET Cutoff and Linear regions JFET Cutoff region In this region, the current flowing from the Drain to the Source terminals of the JFET is zero (ID = 0). |
Power Electronics | |
|---|---|
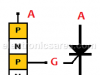 | SCR (Silicon Controlled Rectifier) – ThyristorThe SCR (Silicon Controlled Rectifier) is a 4-layer semiconductor device that works as an almost ideal switch. |
 | DIAC – Diode for Alternating Current. V-I characteristicDIAC is a bidirectional trigger diode, designed to trigger TRIAC and thyristors. DIAC is a voltage-triggered device |
SBS – Silicon Bidirectional SwitchThe SBS is a symmetrical low power device used on trigger applications. It has an additional terminal, which allows you to modify its trigger characteristics with small pulses of current. | |
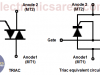 | TRIACTriac is a semiconductor device that belongs to the family of thyristor control devices. It is essentially two SCR connected in parallel and backwards, sharing the same gate. |
 | MOSFET Transistors – NMOS, PMOSMOSFET Transistors or Metal Oxide-Semiconductor (MOS) are field effect devices that use the electric field to create a conduction channel. |
Voltage regulators | |
|---|---|
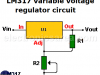 | LM317 Variable Voltage Regulator CircuitLM317 characteristics. How the voltage regulator circuit works, Regulator circuit operation improvement |
 | Increase Output Voltage on 78XX RegulatorsTo understand why the output voltage of an integrated circuit of this type increases, when we place a diode or a resistor at the “Adj” input |