Electronics Area – Electrical and Electronics Tutorials and Circuits
Welcome to Electronics Area
Electrical and Electronics Tutorials and Circuits
Recent posts
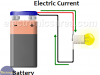
Voltage – Electrical Potential Difference
Potential difference or Voltage is a kind of force that push charges through a conductor. The larger the voltage, the larger the force
What is an Alternating Current?
The difference between an alternating current and a direct current is that a direct current only flows in one direction. Alternating current circulates in one direction, then the opposite direction, and repeats this process continuously.
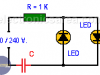
Light-Emitting diode connected to 120/240 VAC
This circuit shows one or two LEDs directly connected to the outlet (120 VAC or 240 VAC). The reduction of the AC input voltage to one that is suitable to use in a LED diode is achieved using a capacitor and a resistor.
Time Delay circuit using Triac and 555 timer
This Time delay circuit using Triac and 555 Timer is very useful when we want to activate or switch on, appliances or devices that work on alternating current (AC), after a preset time.
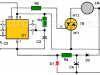
Differential Temperature Controller (PCB)
This circuit measures the temperature difference between 2 sensors and activates a relay when they are different. It is also possible to detect a temperature change, even when the two measured temperatures are normally different.
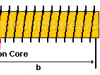
Iron Core Inductor
The iron core inductor has very special magnetic characteristics. What they do is to reinforce the magnetic field. The magnetism of the core material depends on the bias of “the molecular magnetic domains”
Benjamin Franklin’s Fluid Theory
Benjamin Franklin imagined the electricity as a invisible fluid. Franklin assured that if any body had more fluid than usual, it could have a positive charge, but if it had less fluid than normal it had negative charge.
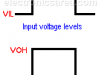
Digital Logic Levels (hight, low, 1, 0)
In digital circuits, it is common to say that we have a “high or a “low” logic level at the input or output of a circuit. If we have a “high” level we say it is a “1” and if we have a “low” level we say that it is a “0”.
LDR – Photoresistor
What is an LDR – Photoresistor? LDR (Light Dependent Resistor) is light sensitive resistor whose resistance changes with the light intensity that falls upon it.
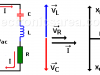
Resonance in an RLC Circuit
Resonance in RLC Circuits is a special condition for parallel and series RLC circuits, when capacitive reactance and inductive reactance have the same magnitude and cancel each other. This only happens at frequency fo.
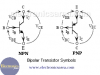
Ebers Moll Model of a Bipolar Transistor
Ebers Moll Model of a Bipolar Transistor
The bipolar transistor is an electronic device that originates a big evolution in the electronics field. The basic features of the bipolar transistor are introduced on this topic. We’ll study the basic model (Ebers Moll Model) of these devices and their use in the analysis of circuits biasing.
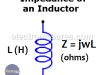
Impedance of Inductor
The impedance of an inductor (also called inductance) is the measure of the opposition to a change of electrical current in this component.