Electronics Area – Electrical and Electronics Tutorials and Circuits
Welcome to Electronics Area
Electrical and Electronics Tutorials and Circuits
Recent posts
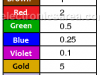
Resistor Tolerance. What is it? – Color code
Resistor tolerance is data that tells us the percentage that can vary the resistor value of its proposed value. This variation may go up or down in the percentage specified tolerance.
What are Microwaves? Applications, Frequency & Wavelength
At the present time the radio frequency spectrum is becoming small for the growing demand for telecommunications. The incursion into the field of microwaves is natural and we must also take into account that there are some applications that are unique to the microwave frequencies.
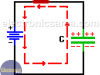
Capacitor and Direct Current (DC) – Dielectric
Capacitor and Direct Current. If a not charged capacitor is connected across the terminals of a battery, a transient current flows as the capacitor plates charge up.
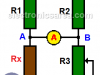
What is the Wheatstone Bridge Circuit?
This circuit was designed in 1833 by Samuel Hunter Christie (1784-1865). However, It was Mr. Charles Wheatstone who gave many uses to the Wheatstone bridge circuit when he discovered it in 1843.
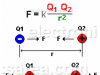
Coulomb’s Law – Electrostatic Force – Formula – Example
Coulomb’s Law – Electrostatic Force – Formula – Example. Learn how to calculate the electrostatic force between 2 electric charges using Coulomb’s Law.
Electronics – Electrical Unit Definitions
Electronics – Electrical Unit Definitions
Definitions of basic measurement units in electricity and electronics. Ampere (A), Coulomb (C), Joule (J), Watt (W), Farad (F), Henry (H), Ohm (Ω), Siemens (S), Volt (V), Hertz (Hz), Radian, Angular frequency (w), Time (t)
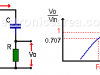
RC High Pass Filter
An RC high pass filter allows only the passage of frequencies above the cut-off frequency (Fc) and eliminates frequencies above this frequency
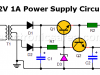
12V 1A Power Supply Circuit
This 12V 1A power supply using zener diode and transistors allows us to obtain an output of approximately 11.4 volts with a very small percentage variation for a wide variety of loads.
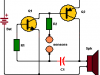
Lie Detector Circuit Using Two Transistors
This simple lie detector consists of two transistors and other additional components and can detect if a person does not tell the truth (the person is lying), using two sensors placed directly on the skin.
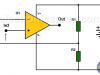
How to use op amps with a single rail power supply?
How to use op amps with a single rail power supply?
Method #1: Voltage divider using two resistors. Method #2: Voltage divider using two Zener diodes.
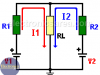
Superposition Theorem – Example
The Superposition Theorem
The Superposition theorem states that the effect of two or more voltage sources in a resistor is equal to the sum of the individual effects of each source taken separately, replacing all the remaining voltage sources with short circuits.
What is Electrical Resistance? Obtaining a material’s resistance
The electrical resistance is a measurement of the opposition that offers a material to the passage of electrons (the electric current)