Electronics Area – Electrical and Electronics Tutorials and Circuits
Welcome to Electronics Area
Electrical and Electronics Tutorials and Circuits
Recent posts
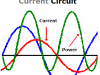
Power in AC Circuit
Electric power. Electrical power on a circuit with reactive load (reactance). How to obtain the current in a circuit having resistance and reactance.
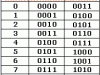
Aiken code – Excess 3 code
Aiken BCD code is similar to the natural BCD code, but with “weights” or “values” distributed differently. The Excess 3 Code is obtained by adding “3” to each combination of the natural BCD code.
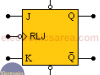
JK Flip-Flop
The JK Flip-Flop is a sequential device with 3 inputs (J, K, CLK (clock signal)) and 2 outputs (Q and Q’). J and K are control inputs.
MOSFET Transistors – NMOS, PMOS
What are MOSFET Transistors?
MOSFET Transistors or Metal Oxide-Semiconductor (MOS) are field effect devices that use the electric field to create a conduction channel. MOSFET transistors are more important than JFETs because almost all Integrated Circuits are built with the MOS technology.
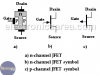
FET – Field Effect Transistor (JFET)
FET (JFET)
Field effect transistor or FET is a particularly interesting transistor and it can be of two types: the Junction Field Effect Transistor or JFET and the Metal-Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET).
Combinational Circuit
A combinational circuit is a circuit where the output depends only on the combination of the inputs at the time we are testing the output
Sequential Circuit – Digital Logic
A sequential circuit is a circuit where there are one or more feed backs from one or more outputs. The new output depend on the inputs and the last output
Logic AND Gate – AND Truth Table
The logic AND gate is one of the simplest gates in Digital Electronics. The output of an AND gate is true (“1”) only when all inputs are true (“1”). If one or more inputs are false (“0”), then the output is false (“0”).
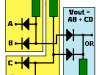
OR and AND logic gates made with diodes
Diode Logic OR gate (wired OR connection) and Diode Logic AND gate (wired AND connection). Diode Logic uses the fact that diodes conduct only in one direction. (they behave like switches)
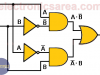
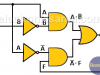
XOR Logic Gate
In digital electronics there are special gates. One of them is the XOR logic gate or exclusive OR gate. Equivalent XOR Logic Gate using common logic gates
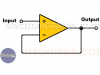
Op Amp Voltage follower / Voltage Buffer
Op-amp voltage follower (op-amp voltage buffer). A buffer has an output that is exactly like the input. This feature is very useful for solving impedance matching problems.
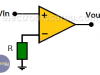
Op Amp Open Loop Gain – Op Amp Open Loop Configuration
Op Amp Open Loop Gain – The open loop gain of the operational amplifier is given when there is no feedback path between the output and either input