Multimeter – VOM – Tester
The multimeter is also known as a tester and VOM. VOM comes from volts, ohms, milliamps, although there are multimeters capable of measuring many other quantities such as capacitance, frequency, temperature, etc.
The multimeter remains the favorite for amateur and for professionals in electronics, because of its price and its accuracy. There are other instruments such as the oscilloscope that is more expensive. There are two types of multimeters: analog and digital.
The analog multimeter
The analog multimeters are easily identified by a needle that moves on a scale indicating the value of the measured quantity.
The digital Multimeter
The digital multimeters are identified mainly by a numeric display in order to read the measured values.
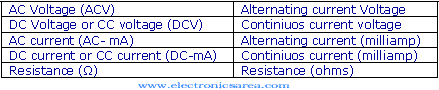
Some of them have a scale selector and others do not. The scale is determined automatically on the multimeter that has no selector scale. The function selector is used to select the type of measure that will be done. For example:
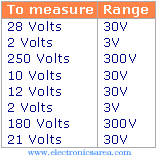
The range selector is used to establish the maximum measurement value that we can display. If you do not have an idea of the magnitude you are going to measure, use the largest range. For example:
Looking at the table above, we can see that we always use a range higher than the magnitude being measured.
You may be interested in: How to protect the 500mA Fuse on a Multimeter?
More Instruments & Measurements Tutorials
- Multimeter - VOM - Tester
- Measuring resistance with an analog multimeter
- Low resistance measurement
- Measuring the resistance of sensitive components
- What is a Wheatstone bridge circuit?
- How to extend analog multimeter voltage range?
- Testing diodes and transistors with a multimeter
- What is a logic probe?
- Scientific Notation - Engineering Notation
- kWh - cost of electrical energy
- DIY circuit diagrams for test equipment