Transformers
Home /
Electrical Transformers Tutorials
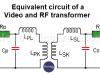
Equivalent transformer circuits (power, audio, video and RF)
Equivalent transformer circuits (power, audio, video and RF). Normally, in the designs and analysis where transformers are used, it is very common to use the characteristics of the transformer as if it were an ideal transformer.
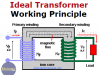
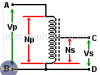
Ideal Transformer Working Principle
Ideal transformer working principle. How the transformer works. Voltage & current transformation ratio. Power ratio between primary & secondary windings
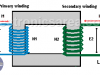
Transformer Turn Ratio (K)
The transformer turn ratio (K) is the quotient value obtained by dividing the number of turns of the primary winding (N1) and the number of turns of the secondary winding (N2). Then K = N1/N2.
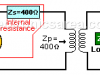
Impedance matching Transformer
An impedance matching transformer is used to couple an antenna to a transmission and / or reception equipment. It was widely used in the coupling of the antenna to the analog television, by radio amateurs
Autotransformer
An autotransformer is a transformer where a part of the winding belongs to both the primary and secondary windings of the transformer. The operating principle is the same as the conventional transformer.
Transformer Structure
Electric Power Transformer Structure. All electric transformers, have three fundamentals parts: high voltage winding, low voltage winding and Core.
Power Transformer usage
The Electric Power Transformer usage. The transformers allow the modification of the voltage and the current values, so they can take the appropriate one to carry and distribute the electric energy.
Why is the core of a transformer laminated?
Why is the core of a transformer laminated? Why it is not possible to use a solid iron core instead of core-laminated? What is Eddy or Foucault’s currents?