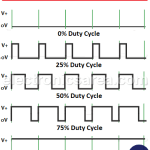
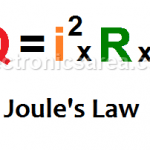PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) is a technique used to control the width of a digital signal in order to adjust the power delivered to certain devices.
Electricity and Electronics – What is the Difference?
The difference between electricity and electronics or the difference of an electric circuit and an electronic circuit, is that in the electronics circuit, a control is exercised over the flow of the electric current.
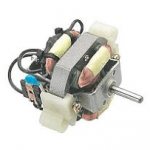
Universal Electric Motor – Construction, Operation, Speed
The universal electric motor is so named because it is the only motor that can be connected to both alternating current and direct current.
Amplifiers and Amplification
Amplifiers and Amplification
Amplifiers are circuits that are used to increase an input signal, thus you can obtain an output signal with much greater amplitude than the original one. Amplification is the process to increase the magnitude of a signal, generally using an amplifier.
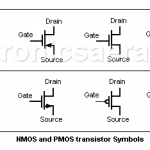
MOSFET Transistors – NMOS, PMOS
What are MOSFET Transistors?
MOSFET Transistors or Metal Oxide-Semiconductor (MOS) are field effect devices that use the electric field to create a conduction channel. MOSFET transistors are more important than JFETs because almost all Integrated Circuits are built with the MOS technology.
Joule’s Law. Joule’s Law formula
What is Joule’s Law?
It is known as Joule effect to the phenomenon by which if in a wire circulates an electrical current, part of the energy is transformed into heat. This law (Joule’s Law) is named after the British physicist James Prescott Joule.
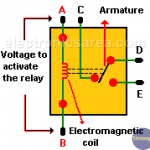
Relay – Electromagnetic Switch
What is a relay?
Relay was invented in 1835 by the US scientist Joseph Henry (1797–1878). Relay or elecromagnetic relay is a magnetically operated switch that is activated or deactivated when the electromagnet is energized.
What are Microwaves? Applications, Frequency & Wavelength
At the present time the radio frequency spectrum is becoming small for the growing demand for telecommunications. The incursion into the field of microwaves is natural and we must also take into account that there are some applications that are unique to the microwave frequencies.
Electronics – Electrical Unit Definitions
Electronics – Electrical Unit Definitions
Definitions of basic measurement units in electricity and electronics. Ampere (A), Coulomb (C), Joule (J), Watt (W), Farad (F), Henry (H), Ohm (Ω), Siemens (S), Volt (V), Hertz (Hz), Radian, Angular frequency (w), Time (t)
DC Motor Counter-electromotive force – Load Effect
Counter-electromotive force or Back-electromotive force
The voltage of a DC motor is divided into a voltage in the windings resistance and a voltage called Counter-electromotive force
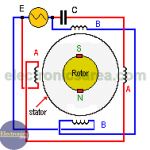
AC motor (AC Electric Motor) – Poles – Windings Relationship
One of the characteristics of an AC motor is the number of rotor poles. This data will automatically give the number of windings that the motor has: # windings = # poles x 2.
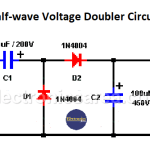
Half-wave Voltage Doubler Circuit with only 2 rectifier diodes.
A half-wave voltage doubler produces twice the DC voltage of a common rectifier. It has a shared line between the input and output terminals.