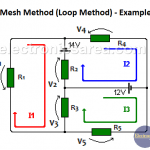
The mesh current method is very useful for finding all the currents in a network. This method, a little more advanced, is also applied to circuits where there are resistances and reactances.
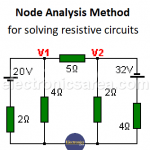
Node Analysis Method – Steps – Example
The node analysis method also known as the nodal analysis is widely used to solve linear resistive circuits (this method, in a slightly extended form, also applies to resistive-reactive circuits)
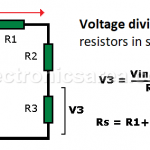
Voltage Divider – Voltage Division – Series Resistors
The voltage divider is a circuit that allows us to obtain an output voltage less than the input voltage. The output voltage is normally obtained across ground and the resistor connected to it, but it could be across any of the other resistors.
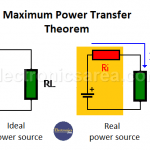
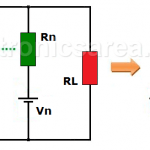
Maximum Power Transfer Theorem Explanation
What does the Maximum Power Transfer Theorem say? “The maximum power transfer to the load is obtained when the load resistance RL is equal to the internal resistance of the source Ri”. But why is that the case? Real voltage sources have the equivalent circuit shown in the figure below, where V = I x […]
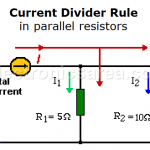
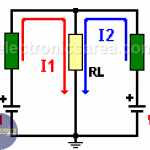
Current Divider Rule in parallel resistors
By using the current divider rule, we can find the current in each resistor connected in parallel. The electric current passing through a circuit of two resistors in parallel is divided in two.
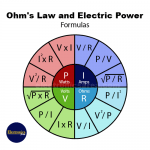
Ohm’s Law and Electric Power – Formulas
Ohm’s law and electrical power. Ohm’s law relates V, I, and R. A more complete expression of Ohm’s law is achieved using the electrical power formula
Millman’s Theorem – Millman’s equivalent circuit
Millman’s theorem is used to directly obtain the voltage between the ends of a parallel branch circuit. Equivalent Millman circuit Formulas, example.
Voltage – Electrical Potential Difference
Potential difference or Voltage is a kind of force that push charges through a conductor. The larger the voltage, the larger the force
Benjamin Franklin’s Fluid Theory
Benjamin Franklin imagined the electricity as a invisible fluid. Franklin assured that if any body had more fluid than usual, it could have a positive charge, but if it had less fluid than normal it had negative charge.
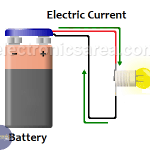
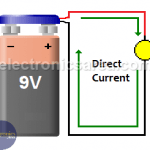
What is Direct Current? – What is DC?
Direct Current (DC), is the result of the flow of electrons (negative charge) in a conductor (most of the time, wires of copper) that goes only in one direction.
Superposition Theorem – Example
The Superposition Theorem
The Superposition theorem states that the effect of two or more voltage sources in a resistor is equal to the sum of the individual effects of each source taken separately, replacing all the remaining voltage sources with short circuits.
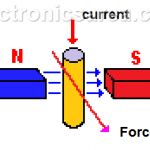
DC Motor – Parts of a DC Motor. Basic Operation Principle.
DC Motor
A DC motor is composed of a stator and a rotor. In many small motors, the stator is composed of magnets. Larger motors have windings.