Resistors Tutorials
Home /
1 – What is a Resistor? 2 – What is resistance?
3 – Resistance and Conductance 4 – More Resistor’s Tutorials
What is a resistor?
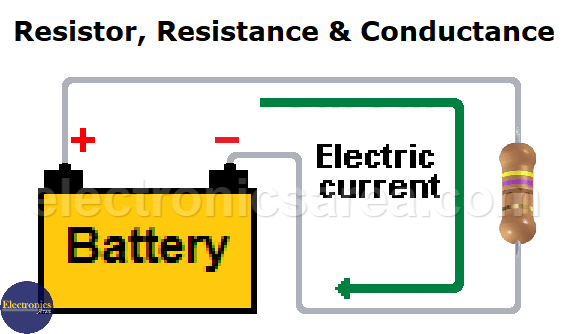
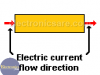
A resistor is an electrical component that resists the flow of electric current. Using Ohm’s law, V = IxR, we can find the voltage across the terminals of resistors. The diagram below shows a light bulb in the path of an electric current.
The most common wattages of resistors are 1/4, 1/2, 1 watt, although larger values are available. The larger the size, the greater the ability of the resistor to dissipate heat. See Joule’s Law.
What is resistance?
Electric current leaves the positive terminal of the battery and returns to the negative terminal by passing through a resistor. Resistors are represented by the capital letter “R” and their values (resistance) are measured in ohms (Ω).
Resistors are manufactured in a wide range of values. There are resistors with values (resistance) of kilo ohms (KΩ), megohms (MΩ).
Kilo ohms (KΩ) and megohms (MΩ) are units used to represent large resistances.
Resistors are primarily made of carbon and come in a wide range of values. There are also surface mount (SMD) resistors of small size.
- 1 Microohm = 1 x 10-6 Ohms (Ω).
- 1 Kilohm (KΩ) = 1 x 103 Ohms.
- 1 Megohm (MΩ) = 1 x 106 Ohms.
- 1 Megohm (MΩ) = 1 x 103 Kilohms (KΩ).
In order to know the value of a resistor without measuring it, there is a resistor color code that helps us to easily obtain its resistance. In order to obtain the resistance of any element of a specific material, it is necessary to know some details of the material such as: its length, cross-sectional area, specific resistance or resistivity of the material that is made.
Resistance and Conductance
Conductance measures the ability of a material to allow an electric current to pass through it. The reciprocal or inverse of resistance is conductance and is generally represented by the capital letter “G”. A circuit with high conductance has low resistance and vice versa. G = 1/R, R = 1/G. Conductance has its units in Siemens
- A resistance of 1 Ohm (Ω) has a conductance of 1 Siemens (S).
- A resistance of 1000 ohms has a conductance of 0.001 Siemens.
- One kilosiemens (1 kS) is equal to one thousand (103) Siemens.
- One megasiemens (1 MS) is equal to one million (106) Siemens.
- One millisiemens (1 mS) is equal to one thousandth (10-3) of a Siemens.
- One microsiemens (1 uS) is equal to one millionth (10-6) of a Siemens.
Note: 1 Siemens = 1 mho (“ohm” spelled backwards)
More resistors Tutorials
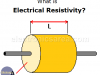
What is Electrical Resistivity?
Electrical resistivity [ρ] (rho) is a characteristic of materials and has ohm-meter unit. Resistivity indicates how much the material opposes the flow of electric current.
Temperature effect on resistance
Temperature effects on resistance. The value of the resistance of a material varies with temperature change. For this reason, the circuit containing these elements should work in controlled environment
Resistor Tolerance. What is it? – Color code
Resistor tolerance is data that tells us the percentage that can vary the resistor value of its proposed value. This variation may go up or down in the percentage specified tolerance.
Resistors in Series – The Equivalent Resistance
Series resistors are those that are connected in series and have the same current flowing or circulating through them
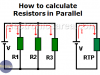
Resistors in Parallel – The equivalent resistance
Resistors in series and parallel. How to calculate resistors in series and resistors in parallel. How to calculate resistors in parallel using conductance. Formulas
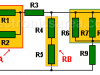
Series/Parallel Resistor Reduction
Series/Parallel Resistor Reduction. Resistors reduction can be done, making some simplifications using resistors in series and resistors in parallel formulas.
What is Electrical Resistance? Obtaining a material’s resistance
The electrical resistance is a measurement of the opposition that offers a material to the passage of electrons (the electric current)
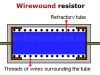
Wirewound Resistor
A wirewound resistor is used when the power to be dissipated is very high. A wire wound resistor is usually coated with a layer of vitreous enamel.
LDR – Photoresistor
What is an LDR – Photoresistor? LDR (Light Dependent Resistor) is light sensitive resistor whose resistance changes with the light intensity that falls upon it.