PWM (Pulse Width Modulation)
Pulse width modulation (PWM) controls the width of a digital signal to adjust the power delivered to certain devices. The width of the active pulse (“ON”) is modified to regulate the amount of current flowing to the device.
How does pulse width modulation (PWM) work?
It functions like a switch that is constantly turning on and off to regulate the amount of current (and therefore power) delivered to the controlled device. These devices can be: DC motors, DC light sources, and other types of devices.
A 12V DC motor receives maximum current and, therefore, maximum power when powered by a 12-volt voltage source. Consequently, it delivers maximum speed at its output (the shaft). (Maximum RPM)
If the same motor is powered by a 0-volt source, however, it receives zero current (0 amps) and zero power (0 watts). Therefore, the speed at its output (the shaft) is zero. (0 RPM).
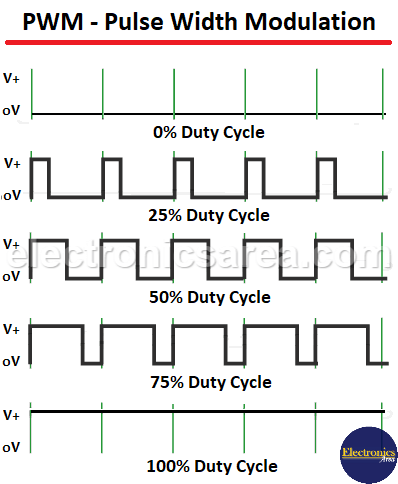
In a pulse width modulation (PWM) system, the motor receives current for a period of time (t1) and then stops receiving it for another period of time (t2). This process repeats continuously. The sum of t1 and t2 is always constant (T = t1 + t2). As t1 increases, t2 decreases proportionally, and vice versa.
Increasing the time (t1) delivers more power, while decreasing it delivers less. To better understand this concept, see the image below.
- If the duty cycle is 0%, then during time t1, the voltage is 0 volts, and the motor is off.
- If the duty cycle is 25%, then 25% of the time t1 is at 12 volts, and 75% of the time it is at 0 volts.
- When the duty cycle is 50%, 50% of the time t1 is at 12 volts, and 50% of the time it is at 0 volts.
- A duty cycle of 75% means that 75% of the time, t1 is at 12 volts, and 25% of the time, it is at 0 volts.
- If the duty cycle is 100%, t1 is at 12V the entire time. This causes the motor to work at maximum capacity because it constantly receives current.
What are the advantages of pulse-width modulation?
The main advantage is energy efficiency. A circuit with this control method delivers a power output to the load that is proportional to the power needed to perform work.
- If a motor’s speed needs to increase, the power delivered to it also increases (higher duty cycle).
- If a motor’s speed needs to be decreased, the power delivered also decreases (lower duty cycle).
What are the applications of pulse width modulation (PWM)?
- Variable speed control for DC motors.
- Dimmers for LED lighting systems
Examples of PWM applications:
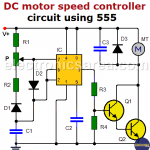
DC Motor Speed Controller Circuit Using a 555
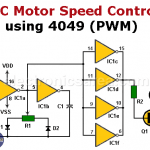
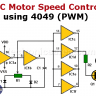
DC Motor Speed Control Using a 4049 Hex Inverter Buffer IC