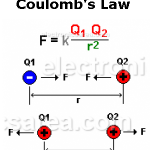
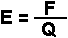Coulomb’s Law – Electrostatic Force – Formula – Example. Learn how to calculate the electrostatic force between 2 electric charges using Coulomb’s Law.
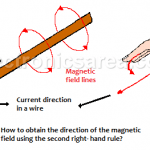
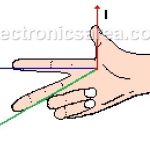
Second Right-Hand Rule – Electromagnetism
Second Right-Hand Rule. When a current flows through a conductive wire, a non-visible effect called the electromagnetic field is generated around it.
First Right Hand Rule
The First Right-hand Rule or (Magnetic Force induced on a Current-Carrying Wire) says that if a current-carrying wire is in the presence of a magnetic field, a force is exerted on the wire.
What’s Static Electricity? – Examples
Static electricity is static, since it is a current that is going nowhere. Both, DC and AC current flow in some direction, but static electricity does not.
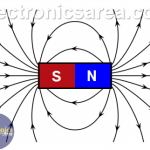
Magnetic Field – Magnetic Field Lines
Magnets. Charges in motion (electric current) behave like magnets (produce magnetic fields)
Electricity and the Structure of Matter: The Bohr Atom
Matter is divided into molecules, which are then divided into atoms. These atoms are composed of two parts: the nucleus and the periphery.
What is an electric charge?
The electron (or proton, since they have the same charge) is the basic unit of electric charge. We can therefore consider the electron as the elementary unit of electric charge.
Polarization of a conducting material
If an electric field is close to a metallic body, part of it is positively charged and other part negatively charged
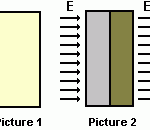
Electric Field: Lines of Force and Electric Field Unit
If a charge Q is subject to an electrostatic force, an electric field exists. If the electric field at a given point is known, the electrostatic force on a charge Q at that point can be found.
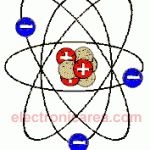
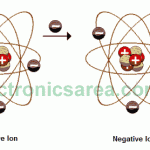
Positive and Negative Charges: Electrons, Protons, Neutrons
If a body has more electrons than protons, it is negatively charged. If it has more protons than electrons it is positively charged