What is a Wirewound Resistor?
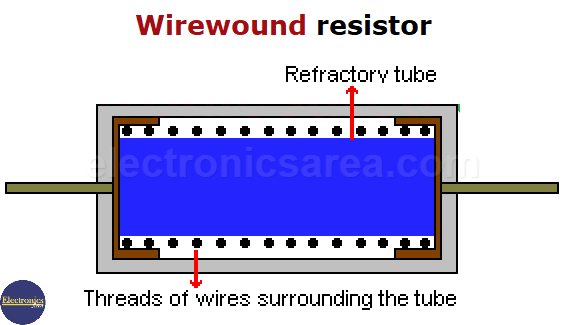
A wirewound resistor is a resistor made with a conductive wire of high resistance. This wire is made of a special alloy and is wound on a support tube made of refractory material such as ceramic, porcelain, etc.
Note: A refractory material doesn’t allow the conduction of heat, on the contrary, it reflects it. The value of a wirewound resistor is determined by the cross-section of the wire, its length, and the resistivity of the alloy.
Why use wire wound resistors?
Wire wound resistors are most often used when the power they must dissipate is very high. After the resistor is manufactured, it is usually coated with a layer of vitreous enamel.
The longer the wire and the larger the cross-section, the greater the heat radiating surface and the greater the power dissipating capacity.
This type of resistor can be compared to the filament of an incandescent lamp, where power is converted to heat (in an incandescent lamp, this power is converted to light and heat).
Wirewound Resistor Values and Power
Wirewound resistors are manufactured with values up to approximately 100 kilohms. This is due to physical dimensional problems. The goal is to get the most heat dissipation in the least amount of space. Wirewound resistors can generally dissipate from 5 watts to 100 watts or more.
The last picture shows a blue refractory tube and threads of wires surrounding it. The black dots represent the wires going in and out of the screen, forming a coil of very tight spring around the tube.
Wirewound resistors are available in fixed and adjustable versions for use as rheostats or potentiometers.
Olli Niemitalo, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
Types of wire wound resistors
Precision Wirewound Resistors
These wirewound resistors are precision resistors because they are made with a wire whose characteristics are known and a very precise resistance value can be obtained.
This type of wirewound resistor has applications in instrumentation. They are often found in multimeters and calibration equipment. Some wirewound resistors have tolerances as low as 0.005%. The power dissipated by this type of resistor is very low.
Power Wirewound Resistors
This type of resistor can dissipate a large amount of power. Some of them have a heat sink to dissipate even more heat.
Additional features of wirewound resistors
- Its construction allows it to be designed to have any value.
- It is very stable over time. Ordinary resistors change their value over time. This type of resistor is very stable over time because of the material it is made of.
- It has great stability against temperature changes. This is achieved by using a wire with a low temperature coefficient of resistance in its manufacture.
- It has the ability to withstand large voltage spikes for short periods of time without damage and without changing its resistance value.